Distributive justice
Equity theory: desire to see equity
- work harder after undeserved reward
- adjust perceptions when can't affect outcome
- blaming the victim
- just world hypothesis
Ultimatum game - people refuse unfair offers
Dictator game - people give some to others
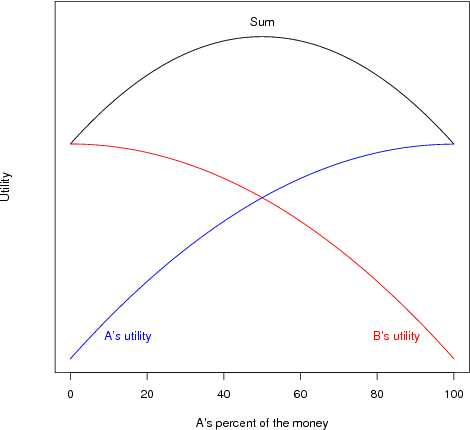
Principles of fairnss: Declininga marginal utility
- Favors equal shares
- Compensation
(insurance, social insurance)
Fairness heuristics and principles
- Equality
- Contribution
- Need
- Maximization
- Compensation
- Punishment and retribution
Cultures differ in their use of these
Non-utilitarian biases: Punishment without deterrence (Baron and Ritov)
A woman who took a new birth control pill has become sterile as a
result of taking the pill, and she brings a complaint against the
ABC Company, which produced the pill. The woman has one child
already, and she is upset and angry because she cannot have
another.
The pills had been tested on several thousand women, all of whom
had had a previous pregnancy and intended to have another. The
effect of the pills on the fertility of the women could therefore
be observed. Other pills had been tested in the same way.
The pills produced various side effects, but they were found to
be safer than all pills made by other companies. A package
insert that came with the pills warned truthfully about several
side effects, but it did not mention sterility because no cases
of sterility had been observed among the women who took the pill
during testing.
Versions A and B.
A. The pill was profitable and the ABC Company knew
that it would be. It was, after all, safer than other pills.
The company knew how to make an even safer pill but had decided
against producing it because the company was not sure that the
safer pill would be profitable. If the company were to stop
making the pill that the woman took, it would make the safer
pill.
B. If the company stopped making this, it would make nothing, and
women would have to use a less save product.
Should the company pay anything to the government in this case?
Why or why not?
Should the woman be compensated by the government? ...?
Version D.
The amount of payment made by the
company was absolutely secret - known only to the government and to a
few trustworthy officials of the company, who were retiring; and the
company was insured by a long-term policy that would cover all
liability costs in full, at a premium set for the industry as a whole
and constant for all companies. These two facts together mean that
decisions about payment to the government could have no effect on
future decisions by this company or other companies about which
vaccines to produce.
Colon cancer screening (Ubel et al.)
- Test 1 saves 1,000 lives.
- Test 2, the more effective and more expensive test, saves
1,100.
- Basic condition: Test 1 given to 100%, test 2 to 50%.
Colon cancer screening (Ubel et al.)
- Test 1 saves 1,000 lives.
- Test 2, the more effective and more expensive test, saves
1,100.
- Basic condition: Test 1 given to 100%, test 2 to 50%.
- In another condition, population expands, so test 1 given to
50% and test 2 to 25%.
Ex post versus ex ante equity (Keller and Sarin, 1988).
| Option | Probability | Person 1 | Person 2 |
| 1 | 1.0 | dies | lives |
| 2 | .5
.5 | lives
dies | dies
lives |
| 3 | .5
.5 | lives
dies | lives
dies |
Equality heuristic: livers (Ubel et al.)
Two groups of 100 waiting for livers:
Group A has 70% chance of survival;
Group B has 30% chance of survival.
You have 100 livers. How do you allocate them to the two groups?
What allocation would maximize survival?
Baron and Jurney, 1993
- Would vote for a 100% tax on
gasoline (to reduce global warming).
- Would it do more good than harm
on the whole?
- Why might you vote against it?
Do no harm (Baron and Jurney, 1993)
- 39% of the subjects said they would vote for a 100% tax on
gasoline (to reduce global warming).
- Of those who would vote
against the tax, 48% thought that it would do more good than harm
on the whole.
- Of those subjects who would vote against the tax,
despite judging that it would do more good than harm, 85% cited
the unfairness of the tax as a reason for voting against it (for
instance, the burden would fall more heavily on people who drive
a lot).
- 75% cited the fact that the tax would harm some
people on the whole (for instance, drivers).
Framing in the perception of harm (Kahneman,
Knetch, and Thaler, 1986b)
A company is making a small profit. It is located in a community
experiencing a recession with substantial unemployment but no
inflation. There are many workers anxious to work at the
company. The company decides to decrease wages and salaries 7%
this year.
62% said company unfair.
A company is making a small profit. It is located in a
community experiencing a recession with substantial unemployment
and inflation of 12%. There are many workers anxious to work at
the company. The company decides to increase wages and salaries
only 5% this year.
22% said company unfair.
Framing in the perception of harm (Kahneman,
Knetch, and Thaler, 1986b)
A company is making a small profit. It is located in a community
experiencing a recession with substantial unemployment but no
inflation. There are many workers anxious to work at the
company. The company decides to decrease wages and salaries 7%
this year.
62% said company unfair.
A company is making a small profit. It is located in a
community experiencing a recession with substantial unemployment
and inflation of 12%. There are many workers anxious to work at
the company. The company decides to increase wages and salaries
only 5% this year.
22% said company unfair.
General principle: Isolation in tax
Schelling effect: bonus for children vs. penalty for childlessness.
Effect of marriage: marriage neutrality, couples neutrality, graduation.
Preference for business taxes
Use of tax to compensate for fixed costs, e.g., health care.
Heuristics and self-interest (van Avermaet, 1974)
- Subjects were instructed to fill out questionnaires until told to
stop.
- Each subject was given either three or six questionnaires and
was told to stop after either 45 or 90 minutes.
- When the subject finished, she
was told that there had been another subject who had had to leave
before he could be told that he was supposed to be paid. The
experimenter, who also said he had to leave, gave the original
subject $7 (in dollar bills and coins) and asked her to send the
other subject his money (in the stamped, addressed envelope
provided).
- Subjects who either worked longer or
completed more questionnaires than the ``other'' gave the other
less than $3.50.
- When the original subjects were equal to the other on
both dimensions, they sent almost exactly $3.50, on the
average.