| Email me | Jennifer Tareila Home |
| Project home |
The Eye |
Back:
Retinal And Rhodopsin |
Next:
Absorption Spectra |
WebMo Job 992 |
Applications |
Links and Refs |
|
http://www.theochem.uni-frankfurt.de/~birgit/Forschung/seite1.html |
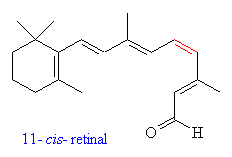
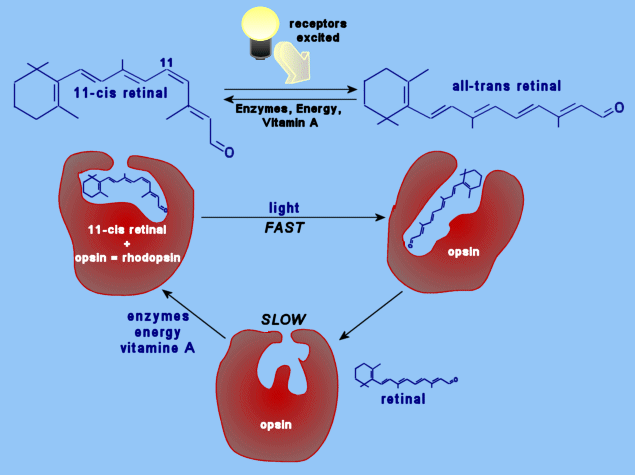
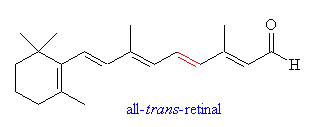
Retinal is a polyene with four
double bonds, and 16 possible isomers. Only 11-cis-retinal is known
to have any photoactivity in organisms. Retinal was first noted in 1933
in photobleached bovine rhodopsin, which was observed to have a λmax of 385nm.
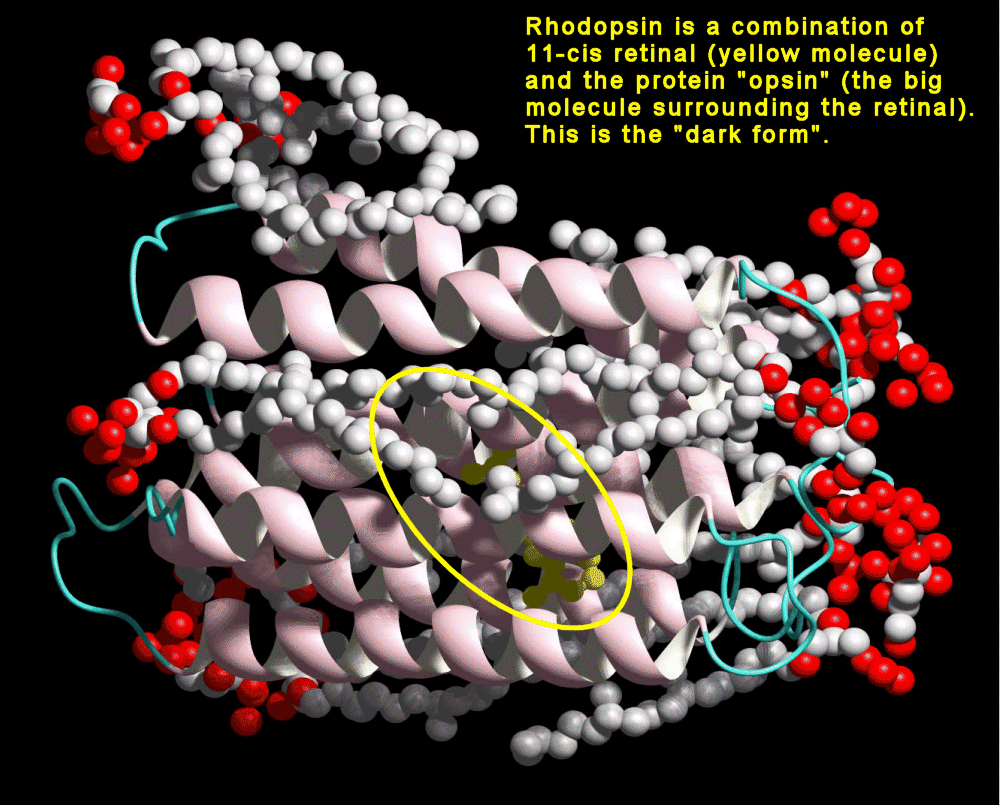
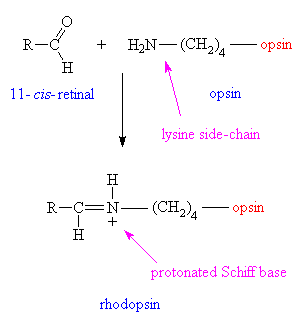
In 1944, the molecule was determined to be a vitamin A derivative. (25) In organisms, retinal is bound to an opsin protein. Rhodopsin, found in humans and other organisms, is a 40kD cross membrane protein with 7α helices and 348 amino acids. The carboxyl terminus resides in the cyctosolic side. There are several different variants on the opsin molecules in organisms, and even slight differences in the cone cells of humans. |
http://webvision.med.utah.edu/photo1.html#pigments |
Rhodopsin, found in humans and
other organisms, is a 40kD cross membrane protein with 7α helices and 348
amino acids. The carboxyl terminus resides in the cyctosolic side.
There are several different variants on the opsin molecules in organisms,
and even slight differences in the cone cells of humans. |
http://www.science.siu.edu/microbiology/micr425/425Notes/09-Halobact.html |
The retinal is bound to the opsin via a protonated
Schiff base. |